💡 Prompting: CO-STAR Framework
CO-STAR framework prompting technique
⭐ The CO-STAR Framework (and Friends)
Prompting is not about clever words — it’s about giving clear intent, right context, and useful constraints.
🧩 What is Prompt Engineering? (In One Breath)
Prompt engineering is the art of telling an AI what you want, how you want it, and for whom — without ambiguity.
Think of it as:
- 🗺️ Giving directions (not guessing games)
- 🧠 Aligning expectations
- 🎯 Reducing surprises in output
🌟 The CO-STAR Framework (One of the Best!)
CO-STAR is a structured prompting framework that ensures:
- clarity
- relevance
- consistency
- predictable quality output
It is especially powerful for beginners because it answers all the questions an AI silently needs.
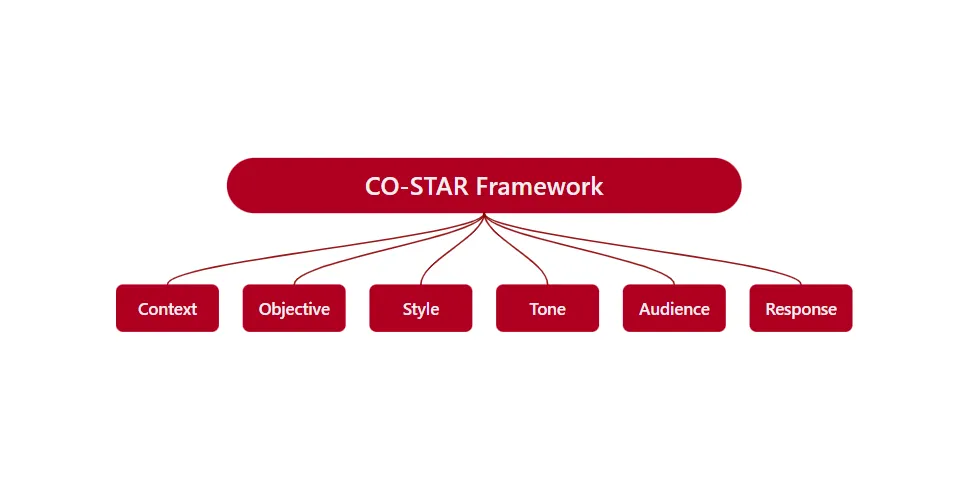
🌟 What is CO-STAR?
CO-STAR is a structured prompting framework that helps you guide LLMs with clarity and intent.
- C — Context
- O — Objective
- S — Style
- T — Tone
- A — Audience
- R — Response format

🧱 CO-STAR — Broken Down Simply
🔹 C — Context
What background does the model need?
- Who you are
- What domain this belongs to
- Any prior assumptions
📌 Why it matters: Without context, the AI guesses.
Example
1
You are an experienced data science instructor teaching beginners.
🔹 O — Objective
What exactly do you want?
- Task
- Goal
- End result
📌 Why it matters: Vague goals → vague answers.
Example
1
Explain the bias–variance tradeoff.
🔹 S — Style
How should it be presented?
- Bullet points?
- Table?
- Story?
- Technical or simple?
📌 Why it matters: Same knowledge, different packaging.
Example
1
Use simple language with examples.
🔹 T — Tone
What emotional or communicative tone?
- Neutral
- Friendly
- Academic
- Chirpy
- Formal
📌 Why it matters: Tone controls readability and engagement.
Example
1
Use a friendly, beginner-friendly tone.
🔹 A — Audience
Who is this for?
- Novice
- Student
- Manager
- Expert
- Child
📌 Why it matters: Good explanations are audience-specific.
Example
1
Assume no prior ML knowledge.
🔹 R — Response (Format & Constraints)
How should the final answer look?
- Length limits
- Sections
- Markdown / code
- Do’s & Don’ts
📌 Why it matters: This avoids over-verbosity or chaos.
Example
1
Limit to 150 words. Use headings and bullet points.
🧪 A Complete CO-STAR Prompt (Example)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Context:
You are an experienced data science instructor.
Objective:
Explain the bias–variance tradeoff.
Style:
Use simple language with a real-world analogy.
Tone:
Friendly and encouraging.
Audience:
Absolute beginners.
Response:
Use bullet points. Avoid formulas. Max 150 words.
✅ Result: Clear, focused, beginner-perfect output.
🏆 Why CO-STAR Is One of the Best Prompting Techniques
✅ Covers all blind spots ✅ Works across any domain ✅ Scales from simple to complex tasks ✅ Ideal for:
- education
- documentation
- technical writing
- curriculum design
- prompt libraries
CO-STAR turns “asking” into “specifying”.
🔁 Other Important Prompting Techniques (Explained Simply)
🎯 Zero-Shot Prompting
Ask directly. No examples.
1
Summarize this article.
✔ Fast ❌ Less reliable for complex tasks
🧩 Few-Shot Prompting
Give examples first.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Example:
Input: Good
Output: Positive
Input: Bad
Output: Negative
Now classify: Amazing
✔ Improves accuracy ✔ Great for classification
🧠 Chain-of-Thought (CoT)
Ask the model to think step-by-step.
1
Explain your reasoning step by step.
✔ Better reasoning ✔ Great for math & logic
⚠️ Use carefully in production (verbosity control)
🧪 Self-Consistency Prompting
Generate multiple answers → pick the best.
1
Solve this problem in 3 different ways and choose the most consistent answer.
✔ Reduces reasoning errors
🔄 Iterative Prompting
Refine outputs gradually.
1
2
3
Rewrite this more concisely.
Now simplify further.
Now make it beginner-friendly.
✔ Mirrors human editing
🛡️ Constraint-Based Prompting
Explicit guardrails.
1
2
3
Do not use jargon.
Do not exceed 100 words.
Do not assume prior knowledge.
✔ Improves safety & clarity
🧭 Role-Based Prompting
Assign an identity.
1
Act as a senior software architect.
✔ Aligns expertise & vocabulary
🧱 CO-STAR vs Others (Quick Comparison)
| Technique | Best For | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-Shot | Simple tasks | ❌ |
| Few-Shot | Pattern learning | ⚠️ |
| CoT | Reasoning | ⚠️ |
| Role-Based | Perspective | ⚠️ |
| CO-STAR | Clarity + control | ✅✅ |
🧠 Final Takeaway (Sticky Insight)
Good prompts reduce thinking load for the model. Great prompts remove ambiguity entirely.
And CO-STAR does exactly that.
⭐ Beginner Recommendation
If you remember only one framework, remember this:
1
Context → Objective → Style → Tone → Audience → Response
That alone will put you ahead of 90% of prompt writers.
🧠 When to Use CO-STAR
- Prompt engineering
- Documentation generation
- AI tutoring
- System instruction design
- Agent workflows
⚑ Takeaway:
CO-STAR brings discipline to creativity — structure without suffocation.
 Prompting: Co-star framework Illustrated!
Prompting: Co-star framework Illustrated!
image: /assets/img/posts/costar_framework.svg
---
layout: post
title: "💡 Prompting: CO-STAR Framework"
description: "CO-STAR framework prompting technique"
author: technical_notes
date: 2025-12-09 00:00:00 +0530
categories: [Notes, CO-STAR]
tags: [CO-STAR, Prompting, Technique, Prompt Engineering]
image:
path: /assets/img/posts/costar_framework.webp
alt: "CO-STAR Framework Diagram"
class: img-center
css: [ "/assets/css/custom.css" ]
toc: true
math: false
mermaid: false
---
{: w="400" h="200" }
_Prompting: Co-star framework Illustrated!_
⚑ Why Log Levels Matter (in Simple Words)
Log levels help organize application messages by importance, so developers can quickly understand what’s happening without drowning in noise.
Think of them like volume controls for information 🔊 — you turn up details when debugging, and turn them down in production.
🧭 Common Log Levels (Most → Least Severe)
- CRITICAL / FATAL – Something went terribly wrong. The app may not continue.
- ERROR – A serious problem affecting functionality that needs fixing.
- WARNING (WARN) – Something looks off; not broken yet, but could become a problem.
- INFO – Normal, useful updates (app started, user logged in, task completed).
- DEBUG – Detailed information for developers to investigate issues.
- TRACE – Extremely fine-grained, step-by-step execution details.
- OFF – Turns logging completely off.
✨ Why Developers Use Log Levels
- Less Noise – See only what matters in production.
- Better Debugging – Enable DEBUG or TRACE when chasing bugs.
- Faster Alerts – Critical errors can trigger emails or notifications.
- Clarity – Clean logs make systems easier to understand and maintain.
🌱 In short: Log levels keep logs useful, readable, and purposeful — quiet when everything is fine, loud when something breaks.