Table of Contents
Introduction
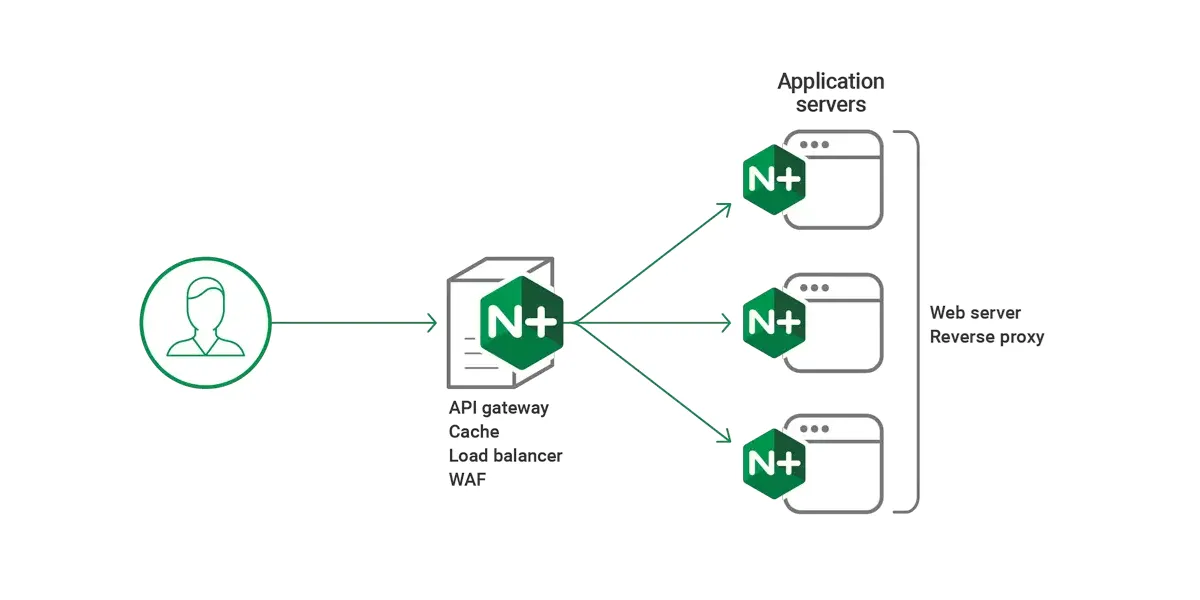
Nginx (pronounced “engine-x”) is a high-performance web server, reverse proxy, load balancer, and HTTP cache. Originally created to solve the C10K problem (handling 10,000 concurrent connections), Nginx uses an asynchronous, event-driven architecture that enables it to handle thousands of concurrent connections with minimal resource consumption.
Key Features
- Event-driven architecture: Non-blocking I/O model for high concurrency
- Low memory footprint: Efficient resource utilization
- Reverse proxy capabilities: Route requests to backend servers
- Load balancing: Distribute traffic across multiple servers
- HTTP caching: Store and serve cached content
- Compression: Reduce bandwidth usage
- SSL/TLS termination: Handle encrypted connections
- FastCGI support: Interface with PHP and other languages
NGINX Features Elucidated!
Nginx Architecture
Process Model
Nginx uses a master-worker process architecture:
Master Process:
- Reads and validates configuration files
- Manages worker processes
- Handles privileged operations (binding to ports)
- Performs graceful upgrades
Worker Processes:
- Handle actual client connections
- Process requests asynchronously
- Each worker is single-threaded but handles multiple connections
- Number of workers typically matches CPU cores
Event-Driven Model
Unlike traditional thread-per-connection models, Nginx uses:
- Event loop: Continuously monitors file descriptors
- Non-blocking I/O: Operations don’t wait for completion
- State machine: Tracks connection states efficiently
- Asynchronous processing: Handles multiple requests concurrently
Terminology & Jargon
Request Processing Lifecycle Terminology
| Common Term | Nginx Equivalent | Description | Usage Context |
|---|
| Phase | Processing Phase | Discrete stage in request handling | Configuration context |
| Stage | Handler Stage | Point where modules process requests | Module development |
| Step | Directive Execution | Individual configuration directive processing | Configuration files |
| Hook | Phase Handler | Function registered for specific phase | Module programming |
| Middleware | Module | Component that processes requests | Architecture discussion |
| Pipeline | Request Processing Chain | Sequential flow through phases | Request lifecycle |
| Filter | Output Filter | Transforms response content | Response modification |
| Handler | Content Handler | Generates response content | Content generation |
Hierarchical Jargon Differentiation
| Level | Term | Scope | Example |
|---|
| Configuration | Context | Top-level configuration block | http, server, location |
| | Block | Nested configuration section | upstream, map, geo |
| | Directive | Individual configuration statement | listen, server_name, proxy_pass |
| | Parameter | Directive argument | Port number, path, variable |
| Architecture | Module | Functional component | HTTP Core, Proxy, FastCGI |
| | Phase | Request processing stage | NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE |
| | Handler | Phase-specific processor | Content handler, access handler |
| | Filter | Response transformation | Header filter, body filter |
| Networking | Connection | TCP connection | Client-to-Nginx connection |
| | Request | HTTP request/response | Individual HTTP transaction |
| | Upstream | Backend connection | Nginx-to-backend connection |
| | Session | Persistent connection state | Keep-alive, SSL session |
Request Processing Phases (Order of Execution)
| Phase Name | Nginx Constant | Purpose | Common Directives |
|---|
| Post-Read | NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE | First phase after reading request | realip module |
| Server Rewrite | NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE | Server-level URL rewriting | rewrite in server block |
| Find Config | NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE | Location matching | Internal only |
| Rewrite | NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE | Location-level URL rewriting | rewrite in location block |
| Post-Rewrite | NGX_HTTP_POST_REWRITE_PHASE | After rewrite processing | Internal only |
| Pre-Access | NGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASE | Pre-access checks | limit_req, limit_conn |
| Access | NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE | Access control | allow, deny, auth_basic |
| Post-Access | NGX_HTTP_POST_ACCESS_PHASE | After access checks | Internal only |
| Try Files | NGX_HTTP_TRY_FILES_PHASE | File existence checks | try_files |
| Content | NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE | Content generation | proxy_pass, fastcgi_pass |
| Log | NGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE | Request logging | access_log, error_log |
Core Concepts
Configuration Structure
Nginx configuration follows a hierarchical context-based structure:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| # Global context
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
# Events context
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
# HTTP context
http {
# HTTP-level directives
# Server context
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
# Location context
location / {
# Location-level directives
}
}
}
|
Context Hierarchy
- Main/Global Context: Top-level configuration
- Events Context: Connection processing configuration
- HTTP Context: HTTP server configuration
- Server Context: Virtual host configuration
- Location Context: URI-specific configuration
- Upstream Context: Backend server pool definition
Variables
Nginx provides built-in variables and supports custom variables:
Request Variables:
$request_method - HTTP method (GET, POST, etc.)$request_uri - Full original request URI$uri - Normalized request URI$args - Query string parameters$query_string - Same as $args
Connection Variables:
$remote_addr - Client IP address$remote_port - Client port$server_addr - Server IP address$server_port - Server port
Response Variables:
$status - Response status code$body_bytes_sent - Response body size$request_time - Request processing time
Custom Variables:
1
2
3
4
5
| set $custom_var "value";
map $http_user_agent $mobile {
default 0;
~*mobile 1;
}
|
FastCGI Configuration
FastCGI (Fast Common Gateway Interface) is a protocol for interfacing web servers with application servers, commonly used with PHP.
Basic FastCGI Setup
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/html;
index index.php index.html;
location ~ \.php$ {
# Security: Prevent processing non-PHP files
try_files $uri =404;
# Pass to PHP-FPM
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock; # Unix socket
# OR
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # TCP socket
# FastCGI parameters
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
|
Essential FastCGI Directives
| Directive | Purpose | Example |
|---|
fastcgi_pass | Backend address | unix:/run/php-fpm.sock |
fastcgi_param | Set FastCGI parameter | fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; |
fastcgi_index | Default file | fastcgi_index index.php; |
fastcgi_split_path_info | Path info parsing | fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$; |
fastcgi_buffers | Response buffering | fastcgi_buffers 16 16k; |
fastcgi_buffer_size | Header buffer size | fastcgi_buffer_size 32k; |
FastCGI Caching
Enable FastCGI caching for dynamic content:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| http {
# Define cache path and settings
fastcgi_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/fastcgi
levels=1:2
keys_zone=FASTCGI_CACHE:100m
inactive=60m
max_size=1g;
fastcgi_cache_key "$scheme$request_method$host$request_uri";
server {
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock;
# Enable caching
fastcgi_cache FASTCGI_CACHE;
fastcgi_cache_valid 200 60m;
fastcgi_cache_valid 404 10m;
fastcgi_cache_methods GET HEAD;
fastcgi_cache_bypass $skip_cache;
fastcgi_no_cache $skip_cache;
# Add cache status header
add_header X-FastCGI-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
}
}
|
FastCGI Optimization Parameters
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| # Buffer configuration
fastcgi_buffers 16 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 64k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 64k;
# Timeouts
fastcgi_connect_timeout 60s;
fastcgi_send_timeout 60s;
fastcgi_read_timeout 60s;
# Connection management
fastcgi_keep_conn on; # Keep connections to FastCGI alive
fastcgi_ignore_client_abort off;
|
Best Practices for FastCGI
- Use Unix sockets when possible: Lower overhead than TCP sockets for local connections
- Implement security checks: Always use
try_files to prevent arbitrary code execution - Enable caching: Cache dynamic content when appropriate
- Optimize buffer sizes: Adjust based on application response sizes
- Connection pooling: Use
fastcgi_keep_conn on for persistent connections - Monitor performance: Track cache hit rates and response times
Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple backend servers to improve reliability, scalability, and performance.
Load Balancing Methods
| Method | Algorithm | Use Case | Configuration |
|---|
| Round Robin | Sequential distribution | Default, equal server capacity | # default |
| Least Connections | Fewest active connections | Varying request processing times | least_conn; |
| IP Hash | Client IP-based routing | Session persistence | ip_hash; |
| Generic Hash | Custom key-based routing | Flexible session affinity | hash $key consistent; |
| Least Time | Lowest response time + connections | Performance-critical (Nginx Plus) | least_time header; |
| Random | Random selection | Simple distribution | random; |
Basic Load Balancer Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| http {
upstream backend {
# Round-robin by default
server backend1.example.com:8080;
server backend2.example.com:8080;
server backend3.example.com:8080;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}
}
|
Advanced Load Balancing Configurations
Least Connections
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| upstream backend {
least_conn;
server backend1.example.com:8080;
server backend2.example.com:8080;
server backend3.example.com:8080;
}
|
IP Hash (Session Persistence)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| upstream backend {
ip_hash;
server backend1.example.com:8080;
server backend2.example.com:8080;
server backend3.example.com:8080;
}
|
Weighted Distribution
1
2
3
4
5
| upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com:8080 weight=3; # 60% of traffic
server backend2.example.com:8080 weight=2; # 40% of traffic
server backend3.example.com:8080 weight=1 backup; # Backup server
}
|
Generic Hash with Consistent Hashing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| upstream backend {
hash $request_uri consistent; # Route based on URI
server backend1.example.com:8080;
server backend2.example.com:8080;
server backend3.example.com:8080;
}
|
Server Parameters
| Parameter | Purpose | Example |
|---|
weight=N | Server weight (default: 1) | weight=5 |
max_fails=N | Failed attempts before marking down (default: 1) | max_fails=3 |
fail_timeout=T | Time to mark server unavailable (default: 10s) | fail_timeout=30s |
backup | Backup server (only used when primary servers down) | backup |
down | Permanently mark server as unavailable | down |
max_conns=N | Maximum concurrent connections | max_conns=100 |
Health Checks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
server backend2.example.com:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
server backend3.example.com:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
# Connection limits
keepalive 32; # Keep 32 idle connections per worker
keepalive_requests 100; # Max requests per connection
keepalive_timeout 60s; # Connection timeout
}
|
Load Balancing Best Practices
- Choose appropriate algorithm: Match algorithm to application requirements
- Set reasonable health check parameters: Balance responsiveness with stability
- Use backup servers: Ensure high availability
- Enable keepalive connections: Reduce connection overhead to backends
- Monitor backend health: Track failed requests and response times
- Implement gradual rollouts: Use weighted distribution for deployments
- Consider session affinity: Use IP hash or hash when sessions matter
Caching Strategies
Nginx can cache both static and dynamic content to reduce backend load and improve response times.
Cache Types
| Type | Purpose | Configuration Directive |
|---|
| Proxy Cache | Cache proxied responses | proxy_cache |
| FastCGI Cache | Cache FastCGI responses | fastcgi_cache |
| uWSGI Cache | Cache uWSGI responses | uwsgi_cache |
| SCGI Cache | Cache SCGI responses | scgi_cache |
Proxy Cache Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| http {
# Define cache path
proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/proxy
levels=1:2
keys_zone=PROXY_CACHE:10m
max_size=1g
inactive=60m
use_temp_path=off;
# Cache key definition
proxy_cache_key "$scheme$request_method$host$request_uri";
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
# Enable caching
proxy_cache PROXY_CACHE;
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m;
proxy_cache_valid 404 1m;
proxy_cache_valid any 5m;
# Cache control
proxy_cache_methods GET HEAD;
proxy_cache_min_uses 2;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout updating http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_cache_background_update on;
proxy_cache_lock on;
# Headers
add_header X-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}
}
|
Cache Path Parameters
| Parameter | Purpose | Example |
|---|
levels | Directory hierarchy depth | levels=1:2 creates /a/bc/... |
keys_zone | Shared memory zone name and size | keys_zone=CACHE:10m |
max_size | Maximum cache size | max_size=10g |
inactive | Remove items not accessed within time | inactive=60m |
use_temp_path | Use separate temp directory | use_temp_path=off (recommended) |
loader_files | Files loaded per cache loader iteration | loader_files=100 |
Cache Control Directives
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_cache PROXY_CACHE;
# Valid response caching
proxy_cache_valid 200 30m;
proxy_cache_valid 404 5m;
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
# Cache bypass conditions
proxy_cache_bypass $http_pragma $http_authorization;
proxy_no_cache $http_pragma $http_authorization;
# Minimum uses before caching
proxy_cache_min_uses 3;
# Stale content serving
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout invalid_header updating http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_cache_background_update on;
# Cache locking
proxy_cache_lock on;
proxy_cache_lock_timeout 5s;
proxy_cache_lock_age 10s;
# Revalidation
proxy_cache_revalidate on;
}
|
Cache Status Values
| Status | Meaning |
|---|
MISS | Response not in cache, fetched from backend |
HIT | Response served from cache |
EXPIRED | Cached item expired, revalidated with backend |
STALE | Expired cached item served due to backend issues |
UPDATING | Stale content served while cache updates |
REVALIDATED | Expired item still valid (304 Not Modified) |
BYPASS | Cache bypassed due to conditions |
Selective Caching with Variables
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| # Define cache bypass conditions
map $request_uri $skip_cache {
default 0;
~*/admin/ 1;
~*/api/user/ 1;
}
map $http_cookie $skip_cache_cookie {
default 0;
~*session 1;
~*logged_in 1;
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_cache PROXY_CACHE;
# Skip cache based on conditions
proxy_cache_bypass $skip_cache $skip_cache_cookie $arg_nocache;
proxy_no_cache $skip_cache $skip_cache_cookie;
}
}
|
Cache Purging
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # Requires ngx_cache_purge module
location ~ /purge(/.*) {
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
deny all;
proxy_cache_purge PROXY_CACHE "$scheme$request_method$host$1";
}
|
Microcaching for Dynamic Content
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| # Cache dynamic content for very short periods
proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/micro
levels=1:2
keys_zone=MICROCACHE:5m
max_size=1g
inactive=1m;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_cache MICROCACHE;
proxy_cache_valid 200 1s; # Cache for 1 second
proxy_cache_use_stale updating;
proxy_cache_background_update on;
proxy_cache_lock on;
}
|
Caching Best Practices
- Use appropriate cache keys: Include relevant request attributes
- Set realistic TTLs: Balance freshness with cache efficiency
- Implement cache bypass: Allow cache invalidation when needed
- Enable stale content serving: Improve availability during backend issues
- Use cache locking: Prevent thundering herd problem
- Monitor cache performance: Track hit ratios and storage usage
- Consider microcaching: Even 1-second caching can dramatically reduce load
- Respect Cache-Control headers: Use
proxy_cache_revalidate on
Compression
Compression reduces bandwidth usage and improves page load times by compressing response bodies before transmission.
Gzip Compression
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| http {
# Enable gzip
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_types
text/plain
text/css
text/xml
text/javascript
application/json
application/javascript
application/xml+rss
application/atom+xml
image/svg+xml;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_disable "msie6";
}
|
Gzip Directives
| Directive | Purpose | Recommended Value |
|---|
gzip | Enable/disable compression | on |
gzip_comp_level | Compression level (1-9) | 5 or 6 |
gzip_types | MIME types to compress | See above list |
gzip_min_length | Minimum response size to compress | 256 |
gzip_vary | Add Vary: Accept-Encoding header | on |
gzip_proxied | Compress proxied responses | any |
gzip_disable | Disable for specific user agents | "msie6" |
gzip_buffers | Number and size of buffers | 16 8k |
Brotli Compression (Requires Module)
Brotli provides better compression than gzip but requires additional module installation.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| http {
# Enable Brotli
brotli on;
brotli_comp_level 6;
brotli_types
text/plain
text/css
text/xml
text/javascript
application/json
application/javascript
application/xml+rss
application/atom+xml
image/svg+xml;
brotli_min_length 256;
# Static Brotli (pre-compressed files)
brotli_static on;
}
|
Pre-compression Strategy
For static content, pre-compress files and serve them directly:
1
2
3
| # Pre-compress files
find /var/www/html -type f \( -name '*.css' -o -name '*.js' -o -name '*.svg' \) -exec gzip -k9 {} \;
find /var/www/html -type f \( -name '*.css' -o -name '*.js' -o -name '*.svg' \) -exec brotli -k {} \;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| location ~* \.(css|js|svg)$ {
# Try to serve pre-compressed version first
gzip_static on;
brotli_static on;
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable";
}
|
Compression Best Practices
- Choose appropriate compression level: Balance CPU usage vs. compression ratio (5-6 is optimal)
- Compress selectively: Only compress text-based formats
- Set minimum size threshold: Skip compression for tiny files (< 256 bytes)
- Use pre-compression for static files: Compress once, serve many times
- Enable Vary header: Ensure proper caching with
gzip_vary on - Consider Brotli: Better compression ratios than gzip
- Avoid double compression: Don’t compress already-compressed formats (images, videos)
Reverse Proxy Configuration
A reverse proxy sits between clients and backend servers, forwarding requests and managing responses.
Basic Reverse Proxy
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend_server:8080;
# Preserve original request headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $server_port;
}
}
|
Essential Proxy Directives
| Directive | Purpose | Recommended Setting |
|---|
proxy_pass | Backend server URL | http://backend:8080 |
proxy_set_header | Set request header | proxy_set_header Host $host; |
proxy_buffering | Enable response buffering | on (default) |
proxy_buffer_size | Header buffer size | 4k or 8k |
proxy_buffers | Response body buffers | 8 4k or 8 8k |
proxy_busy_buffers_size | Size for sending to client | 16k |
proxy_connect_timeout | Backend connection timeout | 60s |
proxy_send_timeout | Sending request timeout | 60s |
proxy_read_timeout | Reading response timeout | 60s |
Advanced Proxy Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
# Headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Buffering
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 8 4k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 16k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 1024m;
# Timeouts
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
# HTTP version and connection handling
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
# Error handling
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_next_upstream_tries 3;
proxy_next_upstream_timeout 10s;
# Redirects
proxy_redirect off;
# Request body
client_max_body_size 100m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
}
|
WebSocket Proxying
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| location /websocket/ {
proxy_pass http://backend;
# WebSocket-specific headers
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
# Standard headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
# Timeouts for long-lived connections
proxy_read_timeout 3600s;
proxy_send_timeout 3600s;
}
|
SSL/TLS Termination
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name example.com;
# SSL certificates
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.key;
# SSL configuration
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# SSL session caching
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
# HSTS
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains" always;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}
|
Proxy Caching Integration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| http {
proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/proxy
levels=1:2
keys_zone=PROXY_CACHE:10m
max_size=1g
inactive=60m;
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_cache PROXY_CACHE;
proxy_cache_valid 200 10m;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout updating http_500 http_502 http_503;
add_header X-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}
}
|
Reverse Proxy Best Practices
- Set proper headers: Always forward client information to backends
- Configure appropriate timeouts: Balance responsiveness with long operations
- Enable HTTP/2: Improve performance for modern clients
- Use connection pooling: Set
proxy_http_version 1.1 and Connection "" - Implement error handling: Use
proxy_next_upstream for failover - Buffer wisely: Enable buffering for most cases, disable for streaming
- Secure connections: Implement SSL/TLS termination with strong ciphers
Routing to Backend Applications
Routing to Node.js Applications
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| upstream nodejs_backend {
least_conn;
server 127.0.0.1:3000;
server 127.0.0.1:3001;
server 127.0.0.1:3002;
keepalive 64;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name nodeapp.example.com;
# Logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/nodeapp_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/nodeapp_error.log;
# Static files (if any)
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|eot)$ {
root /var/www/nodeapp/public;
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable";
}
# Proxy to Node.js
location / {
proxy_pass http://nodejs_backend;
# Headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# WebSocket support
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
# Timeouts
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
# Buffering
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 8 4k;
}
# Health check endpoint
location /health {
access_log off;
proxy_pass http://nodejs_backend/health;
}
}
|
Routing to Java Spring Boot Applications
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| upstream springboot_backend {
server 127.0.0.1:8080;
server 127.0.0.1:8081;
server 127.0.0.1:8082;
keepalive 32;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name springapp.example.com;
# Logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/springapp_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/springapp_error.log;
# Increase max body size for file uploads
client_max_body_size 50m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
# Static resources (if served by Spring Boot)
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|eot)$ {
proxy_pass http://springboot_backend;
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable";
}
# API endpoints
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://springboot_backend;
# Headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Prefix /api;
# HTTP/1.1 for keepalive
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
# Timeouts (adjust for long-running operations)
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 120s;
proxy_read_timeout 120s;
# Buffering
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffer_size 8k;
proxy_buffers 16 8k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;
}
# Main application
location / {
proxy_pass http://springboot_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
}
# Actuator endpoints (Spring Boot monitoring)
location /actuator/ {
allow 192.168.1.0/24; # Internal network only
deny all;
proxy_pass http://springboot_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
|
Multi-Application Routing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| # Route different paths to different backends
server {
listen 80;
server_name app.example.com;
# Node.js frontend
location / {
proxy_pass http://nodejs_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
}
# Spring Boot API
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://springboot_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
}
# Python microservice
location /analytics/ {
proxy_pass http://python_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
|
Subdomain-Based Routing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| # Node.js application
server {
listen 80;
server_name node.example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://nodejs_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
# Spring Boot application
server {
listen 80;
server_name api.example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://springboot_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
|
Best Practices for Application Routing
- Use appropriate load balancing: Choose algorithm based on application characteristics
- Enable keepalive connections: Reduce connection overhead to backends
- Set realistic timeouts: Consider application processing time
- Handle static assets efficiently: Serve directly or cache aggressively
- Implement health checks: Monitor backend application health
- Configure proper logging: Track requests and errors per application
- Secure sensitive endpoints: Restrict access to admin/actuator endpoints
- Support WebSockets when needed: Configure proper headers for real-time features
Worker Process Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| # Typically set to number of CPU cores
worker_processes auto;
# Increase system limits
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events {
# Maximum connections per worker
worker_connections 4096;
# Use epoll on Linux for better performance
use epoll;
# Accept multiple connections at once
multi_accept on;
}
|
Buffer Optimization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| http {
# Client request buffers
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_header_buffer_size 1k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 8k;
# Output buffers
output_buffers 1 32k;
postpone_output 1460;
# Proxy buffers
proxy_buffer_size 8k;
proxy_buffers 8 8k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 16k;
# FastCGI buffers
fastcgi_buffer_size 8k;
fastcgi_buffers 8 8k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 16k;
}
|
Timeout Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| http {
# Client timeouts
client_body_timeout 12s;
client_header_timeout 12s;
send_timeout 10s;
# Keepalive
keepalive_timeout 65s;
keepalive_requests 100;
# Proxy timeouts
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
# FastCGI timeouts
fastcgi_connect_timeout 60s;
fastcgi_send_timeout 60s;
fastcgi_read_timeout 60s;
}
|
Connection Optimization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| http {
# Reset timed out connections
reset_timedout_connection on;
# TCP optimization
tcp_nodelay on;
tcp_nopush on;
# Sendfile for static content
sendfile on;
sendfile_max_chunk 512k;
# AIO for large files
aio threads;
aio_write on;
}
|
Static Content Optimization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|eot|pdf)$ {
# Serve directly
root /var/www/html;
# Enable sendfile
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
# Open file cache
open_file_cache max=10000 inactive=30s;
open_file_cache_valid 60s;
open_file_cache_min_uses 2;
open_file_cache_errors on;
# Long expiration
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable";
# Gzip
gzip_static on;
# Access log (disable for performance)
access_log off;
}
|
Open File Cache
1
2
3
4
5
6
| http {
open_file_cache max=10000 inactive=30s;
open_file_cache_valid 60s;
open_file_cache_min_uses 2;
open_file_cache_errors on;
}
|
HTTP/2 Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
# HTTP/2 specific settings
http2_max_field_size 16k;
http2_max_header_size 32k;
http2_max_requests 1000;
# HTTP/2 push
location = /index.html {
http2_push /css/style.css;
http2_push /js/app.js;
}
}
|
Rate Limiting
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| http {
# Define rate limit zones
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=general:10m rate=10r/s;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=api:10m rate=5r/s;
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
server {
# Apply rate limits
location / {
limit_req zone=general burst=20 nodelay;
limit_conn addr 10;
}
location /api/ {
limit_req zone=api burst=10 nodelay;
limit_conn addr 5;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| # Stub status module
location /nginx_status {
stub_status;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}
|
| Optimization | Impact | Configuration |
|---|
| Worker processes | High | worker_processes auto; |
| Worker connections | High | worker_connections 4096; |
| Sendfile | High | sendfile on; |
| TCP optimization | Medium | tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; |
| Gzip compression | High | gzip on; gzip_comp_level 6; |
| Open file cache | Medium | open_file_cache max=10000; |
| Keepalive | Medium | keepalive_timeout 65s; |
| HTTP/2 | High | listen 443 ssl http2; |
| Buffer sizes | Medium | Adjust based on workload |
| Rate limiting | Variable | Protect against abuse |
Security Best Practices
Hide Nginx Version
1
2
3
| http {
server_tokens off;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| server {
# Prevent clickjacking
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
# Prevent MIME sniffing
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
# XSS protection
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
# Referrer policy
add_header Referrer-Policy "strict-origin-when-cross-origin" always;
# Content Security Policy
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';" always;
# HSTS (only for HTTPS)
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
# Permissions Policy
add_header Permissions-Policy "geolocation=(), microphone=(), camera=()" always;
}
|
SSL/TLS Best Practices
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
# Certificates
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/key.pem;
# Modern SSL configuration
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# DH parameters
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
# Session caching
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/chain.pem;
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 valid=300s;
resolver_timeout 5s;
}
|
Access Control
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| # IP-based restrictions
location /admin/ {
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.0.0.0/8;
deny all;
}
# HTTP Basic Authentication
location /protected/ {
auth_basic "Restricted Area";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
}
# Geographic restrictions (requires GeoIP module)
geo $allowed_country {
default no;
US yes;
CA yes;
GB yes;
}
server {
if ($allowed_country = no) {
return 403;
}
}
|
Request Filtering
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| # Block specific user agents
if ($http_user_agent ~* (bot|crawler|spider|scraper)) {
return 403;
}
# Block specific request methods
if ($request_method !~ ^(GET|POST|HEAD)$) {
return 405;
}
# Prevent access to hidden files
location ~ /\. {
deny all;
access_log off;
log_not_found off;
}
# Prevent PHP execution in uploads
location ~* /uploads/.*\.php$ {
deny all;
}
|
DDoS Protection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| http {
# Connection limits
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
limit_conn_status 429;
# Request rate limits
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=10r/s;
limit_req_status 429;
server {
location / {
limit_conn addr 10;
limit_req zone=one burst=20 nodelay;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| # Reject malformed requests
if ($request_uri ~* "(;|<|>|'|\"|\)|%0A|%0D|%27|%3C|%3E|%00)") {
return 400;
}
# Limit request body size
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
# Limit URL length
large_client_header_buffers 2 1k;
|
Security Monitoring
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # Detailed error logging
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
# Access logging with security info
log_format security '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] '
'"$request" $status $body_bytes_sent '
'"$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" '
'$request_time $upstream_response_time';
access_log /var/log/nginx/security.log security;
|
Security Checklist
| Security Measure | Implementation |
|---|
| Hide server version | server_tokens off; |
| SSL/TLS only | Redirect HTTP to HTTPS |
| Strong ciphers | Use modern cipher suites |
| Security headers | X-Frame-Options, CSP, HSTS |
| Rate limiting | Protect against brute force |
| Access control | IP whitelisting, authentication |
| Input validation | Filter malicious requests |
| File upload security | Restrict execution in upload directories |
| Regular updates | Keep Nginx and modules updated |
| Monitor logs | Track suspicious activity |
URL Rewriting and Redirects
URL rewriting is used to modify request URIs, implement redirects, and control request flow.
Rewrite Directive
The rewrite directive uses PCRE regular expressions to modify URIs.
Syntax: rewrite regex replacement [flag];
Rewrite Flags
| Flag | Behavior | Use Case |
|---|
last | Stop processing current block, search for new location | Internal rewrites |
break | Stop processing rewrite directives | Prevent rewrite loops |
redirect | Return 302 temporary redirect | Temporary URL changes |
permanent | Return 301 permanent redirect | Permanent URL changes |
Common Rewrite Examples
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
# HTTP to HTTPS redirect
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
# Force non-www to www
if ($host = 'www.example.com') {
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
# Rewrite old URL structure to new
rewrite ^/old-page$ /new-page permanent;
rewrite ^/blog/([0-9]+)/(.+)$ /article/$1/$2 permanent;
# Remove trailing slash
rewrite ^/(.*)/$ /$1 permanent;
# Remove .php extension
rewrite ^/(.+)\.php$ /$1 permanent;
location / {
# Try files, then directory, then fallback to index.php
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
}
|
Return Directive (Preferred)
The return directive is more efficient than rewrite for simple redirects.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| # Simple redirect
location /old-url {
return 301 /new-url;
}
# Redirect with variables
location /download {
return 302 https://downloads.example.com$request_uri;
}
# Return custom response
location /maintenance {
return 503 "Site under maintenance";
}
# Conditional redirects
if ($request_method !~ ^(GET|POST)$) {
return 405;
}
|
Try Files Directive
try_files checks for file existence before processing.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| # WordPress permalinks
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
# Static files with fallback
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ @backend;
}
location @backend {
proxy_pass http://backend_server;
}
# Multiple fallbacks
location /images/ {
try_files $uri $uri/ /placeholder.png =404;
}
|
Map Directive
Create conditional variables based on other variables.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| # Mobile detection
map $http_user_agent $is_mobile {
default 0;
~*mobile 1;
~*android 1;
~*iphone 1;
}
server {
location / {
if ($is_mobile) {
rewrite ^ https://m.example.com$request_uri permanent;
}
}
}
# Environment-based routing
map $host $backend {
dev.example.com dev_backend;
staging.example.com staging_backend;
default prod_backend;
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://$backend;
}
}
|
Rewrite Best Practices
- Prefer
return over rewrite: More efficient for simple redirects - Use
try_files instead of if: Avoid if directive when possible - Limit rewrite loops: Nginx limits to 10 internal redirects
- Use specific regex patterns: More efficient than broad patterns
- Test thoroughly: Rewrite rules can have unexpected consequences
- Document complex rules: Comment your rewrite logic
- Use
last flag carefully: Can cause performance issues if overused
Logging and Monitoring
Comprehensive logging and monitoring are essential for troubleshooting, performance analysis, and security.
Access Log Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| http {
# Default combined format
log_format combined '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] '
'"$request" $status $body_bytes_sent '
'"$http_referer" "$http_user_agent"';
# Custom detailed format
log_format detailed '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] '
'"$request" $status $body_bytes_sent '
'"$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" '
'rt=$request_time uct="$upstream_connect_time" '
'uht="$upstream_header_time" urt="$upstream_response_time"';
# JSON format for log aggregation
log_format json escape=json '{'
'"time_local":"$time_local",'
'"remote_addr":"$remote_addr",'
'"remote_user":"$remote_user",'
'"request":"$request",'
'"status": "$status",'
'"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent",'
'"request_time":"$request_time",'
'"http_referrer":"$http_referer",'
'"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent"'
'}';
# Performance monitoring format
log_format performance '$remote_addr [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent '
'rt=$request_time uct=$upstream_connect_time '
'uht=$upstream_header_time urt=$upstream_response_time '
'cache=$upstream_cache_status';
server {
# Enable access logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log detailed;
# Multiple logs
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log combined;
access_log /var/log/nginx/performance.log performance;
# Buffered logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log combined buffer=32k flush=5s;
# Conditional logging
map $status $loggable {
~^[23] 0; # Don't log 2xx and 3xx
default 1;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/errors.log combined if=$loggable;
}
}
|
Error Log Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| # Global error log
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
http {
# HTTP-level error log
error_log /var/log/nginx/http_error.log error;
server {
# Server-level error log
error_log /var/log/nginx/example.com_error.log notice;
location /api/ {
# Location-level error log
error_log /var/log/nginx/api_error.log debug;
}
}
}
|
Error Log Severity Levels
| Level | Description | When to Use |
|---|
debug | Debugging information | Development only |
info | Informational messages | Detailed monitoring |
notice | Normal but significant | General monitoring |
warn | Warning messages | Potential issues |
error | Error conditions | Default level |
crit | Critical conditions | Serious problems |
alert | Action must be taken | Immediate attention |
emerg | System unusable | Emergency situations |
Conditional Logging
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| http {
# Skip logging for health checks
map $request_uri $loggable {
/health 0;
/status 0;
/ping 0;
default 1;
}
# Skip logging for specific IPs
map $remote_addr $log_ip {
127.0.0.1 0;
10.0.0.0/8 0;
default 1;
}
# Combined conditions
map "$loggable:$log_ip" $do_log {
"0:~" 0;
"~:0" 0;
default 1;
}
server {
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log combined if=$do_log;
}
}
|
Log Rotation
Create /etc/logrotate.d/nginx:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| /var/log/nginx/*.log {
daily
missingok
rotate 14
compress
delaycompress
notifempty
create 0640 nginx nginx
sharedscripts
postrotate
[ -f /var/run/nginx.pid ] && kill -USR1 `cat /var/run/nginx.pid`
endscript
}
|
Real-time Monitoring
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # Enable stub_status module
location /nginx_status {
stub_status;
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow 10.0.0.0/8;
deny all;
}
|
Output format:
1
2
3
4
| Active connections: 291
server accepts handled requests
16630948 16630948 31070465
Reading: 6 Writing: 179 Waiting: 106
|
Monitoring Metrics to Track
| Metric | Description | Command/Tool |
|---|
| Active connections | Current client connections | stub_status |
| Requests per second | Throughput measurement | Log analysis |
| Response time | Performance indicator | $request_time |
| Error rate | 4xx/5xx responses | Status code analysis |
| Cache hit ratio | Cache effectiveness | $upstream_cache_status |
| Upstream response time | Backend performance | $upstream_response_time |
| SSL handshake time | SSL performance | Custom logging |
Log Analysis Commands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| # Top 10 requested URLs
awk '{print $7}' /var/log/nginx/access.log | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn | head -10
# Top 10 client IPs
awk '{print $1}' /var/log/nginx/access.log | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn | head -10
# Status code distribution
awk '{print $9}' /var/log/nginx/access.log | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn
# Average request time
awk '{sum+=$NF; count++} END {print sum/count}' /var/log/nginx/access.log
# Requests per hour
awk '{print $4}' /var/log/nginx/access.log | cut -d: -f2 | sort | uniq -c
# 404 errors
awk '($9 ~ /404/)' /var/log/nginx/access.log | awk '{print $7}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn
# Slow requests (> 1 second)
awk '($NF > 1.000) {print $0}' /var/log/nginx/access.log
|
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue: 502 Bad Gateway
Causes:
- Backend server is down
- Connection timeout to backend
- Backend returning invalid response
- SELinux blocking connections
Solutions:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| # Increase timeouts
proxy_connect_timeout 75s;
proxy_send_timeout 75s;
proxy_read_timeout 75s;
# Add more upstream servers
upstream backend {
server backend1:8080;
server backend2:8080 backup;
}
# Check SELinux
# setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1
|
Diagnostics:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # Check backend connectivity
curl -v http://backend:8080
# Check Nginx error log
tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
# Check backend logs
journalctl -u backend-service -f
|
Issue: 504 Gateway Timeout
Causes:
- Backend processing taking too long
- Network issues
- Insufficient resources
Solutions:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| # Increase timeout values
proxy_read_timeout 300s;
proxy_connect_timeout 300s;
proxy_send_timeout 300s;
# Enable keepalive to backends
upstream backend {
server backend:8080;
keepalive 32;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
}
|
Issue: High CPU Usage
Causes:
- Too many worker processes
- Regex-heavy rewrites
- Inefficient configurations
- SSL/TLS overhead
Solutions:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| # Optimize worker configuration
worker_processes auto; # Match CPU cores
worker_connections 1024; # Adjust based on load
# Enable caching
open_file_cache max=10000 inactive=30s;
open_file_cache_valid 60s;
# Use efficient rewrites
# Bad: Multiple rewrite rules
# Good: Single return directive
location /old {
return 301 /new;
}
# Enable HTTP/2
listen 443 ssl http2;
|
Issue: Connection Refused
Causes:
- Nginx not running
- Firewall blocking
- Incorrect port configuration
- SELinux policies
Solutions:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| # Check Nginx status
systemctl status nginx
# Check listening ports
ss -tlnp | grep nginx
# Test configuration
nginx -t
# Check firewall
firewall-cmd --list-all
# Check SELinux
sestatus
ausearch -m avc -ts recent
|
Issue: SSL Certificate Errors
Causes:
- Expired certificate
- Incorrect certificate chain
- Wrong domain name
- Cipher mismatch
Solutions:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # Proper SSL configuration
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/chain.pem;
# Modern SSL configuration
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
|
Diagnostics:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # Test SSL configuration
openssl s_client -connect example.com:443 -servername example.com
# Check certificate expiry
echo | openssl s_client -connect example.com:443 2>/dev/null | openssl x509 -noout -dates
# Verify certificate chain
openssl verify -CAfile chain.pem fullchain.pem
|
Debugging Tips
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| # Enable debug logging
error_log /var/log/nginx/debug.log debug;
# Add debugging headers
add_header X-Debug-Upstream $upstream_addr;
add_header X-Debug-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
add_header X-Debug-Time $request_time;
# Log request body (for debugging only)
client_body_in_file_only on;
client_body_temp_path /tmp/nginx;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| # Check active connections
netstat -an | grep :80 | wc -l
# Monitor Nginx status
watch -n 1 'curl -s http://localhost/nginx_status'
# Check file descriptor usage
lsof -p $(cat /var/run/nginx.pid) | wc -l
# Monitor error rate
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log | grep " 50[0-9] "
# Real-time request analysis
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log | awk '{print $9, $7}' | sort | uniq -c
|
Advanced Topics
Nginx Modules
Core Modules (Always Available)
| Module | Purpose | Key Directives |
|---|
| ngx_http_core_module | Core HTTP functionality | location, server, listen |
| ngx_http_rewrite_module | URL rewriting | rewrite, return, set |
| ngx_http_proxy_module | Reverse proxy | proxy_pass, proxy_set_header |
| ngx_http_fastcgi_module | FastCGI support | fastcgi_pass, fastcgi_param |
| ngx_http_ssl_module | SSL/TLS support | ssl_certificate, ssl_protocols |
Optional Modules (Compile-time)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # Check compiled modules
nginx -V 2>&1 | tr ' ' '\n' | grep module
# Common optional modules:
# --with-http_gzip_static_module
# --with-http_realip_module
# --with-http_stub_status_module
# --with-http_ssl_module
# --with-http_v2_module
# --with-stream (TCP/UDP load balancing)
|
Nginx Plus Features
Commercial version with additional capabilities:
- Dynamic reconfiguration: Update upstream servers without reload
- Active health checks: Proactive backend monitoring
- Advanced load balancing: Least time, session persistence
- Real-time monitoring: Dashboard with detailed metrics
- JWT authentication: Native JWT validation
- Key-value store: Shared memory storage
- Geographic load balancing: DNS-based routing
Stream Module (TCP/UDP Load Balancing)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| stream {
upstream mysql_backend {
server mysql1:3306;
server mysql2:3306;
}
upstream dns_backend {
server dns1:53;
server dns2:53;
}
server {
listen 3306;
proxy_pass mysql_backend;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
}
server {
listen 53 udp;
proxy_pass dns_backend;
proxy_responses 1;
proxy_timeout 20s;
}
}
|
A/B Testing and Canary Deployments
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| # Split traffic based on cookie
map $cookie_version $backend {
"beta" beta_backend;
default prod_backend;
}
# Percentage-based splitting
split_clients "${remote_addr}" $backend {
10% beta_backend; # 10% to beta
* prod_backend; # 90% to production
}
upstream prod_backend {
server prod1:8080;
server prod2:8080;
}
upstream beta_backend {
server beta1:8080;
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://$backend;
}
}
|
GeoIP-based Routing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| http {
geoip_country /usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIP.dat;
geoip_city /usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat;
map $geoip_country_code $nearest_server {
default us_backend;
CN cn_backend;
JP jp_backend;
GB eu_backend;
DE eu_backend;
FR eu_backend;
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://$nearest_server;
}
}
}
|
Request Limiting and Throttling
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| http {
# Define limit zones
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=general:10m rate=10r/s;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=api:10m rate=5r/s;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=login:10m rate=1r/m;
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
# Return custom error page
limit_req_status 429;
limit_conn_status 429;
server {
# General rate limiting
location / {
limit_req zone=general burst=20 nodelay;
limit_conn addr 10;
}
# Strict API rate limiting
location /api/ {
limit_req zone=api burst=10 nodelay;
limit_req_status 429;
}
# Very strict login rate limiting
location /login {
limit_req zone=login burst=2;
}
# Custom 429 error page
error_page 429 /429.html;
location = /429.html {
internal;
return 429 "Too many requests. Please try again later.\n";
}
}
}
|
Nginx Configuration Testing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| # Test configuration syntax
nginx -t
# Test and show configuration
nginx -T
# Test with specific config file
nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# Check configuration dump
nginx -T | less
# Reload configuration
nginx -s reload
# Graceful shutdown
nginx -s quit
# Fast shutdown
nginx -s stop
# Reopen log files
nginx -s reopen
|
Containerization and Orchestration
Docker Deployment
Basic Nginx Docker Container
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| # Dockerfile
FROM nginx:latest
# Copy custom configuration
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
COPY default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
# Copy static content
COPY html /usr/share/nginx/html
# Expose ports
EXPOSE 80 443
# Health check
HEALTHCHECK --interval=30s --timeout=3s \
CMD curl -f http://localhost/ || exit 1
|
Building and Running
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| # Build image
docker build -t my-nginx:latest .
# Run container
docker run -d \
--name nginx-server \
-p 80:80 \
-p 443:443 \
-v /path/to/content:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro \
-v /path/to/config:/etc/nginx/conf.d:ro \
my-nginx:latest
# View logs
docker logs -f nginx-server
# Execute commands
docker exec -it nginx-server nginx -t
docker exec -it nginx-server nginx -s reload
|
Docker Compose Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| version: '3.8'
services:
nginx:
image: nginx:latest
container_name: nginx-server
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:ro
- ./conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d:ro
- ./html:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro
- ./ssl:/etc/nginx/ssl:ro
- ./logs:/var/log/nginx
networks:
- webnet
restart: unless-stopped
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost/"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 3s
retries: 3
backend:
image: node:18
container_name: backend-app
working_dir: /app
volumes:
- ./app:/app
command: npm start
networks:
- webnet
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
webnet:
driver: bridge
|
Multi-Stage Docker Build
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| # Build stage
FROM node:18 AS builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm ci
COPY . .
RUN npm run build
# Production stage
FROM nginx:alpine
COPY --from=builder /app/dist /usr/share/nginx/html
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
EXPOSE 80
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
|
Kubernetes Deployment
Basic Deployment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| # nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.25
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "100m"
limits:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "200m"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
|
Service Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| # nginx-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
name: http
- protocol: TCP
port: 443
targetPort: 443
name: https
|
ConfigMap for Nginx Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| # nginx-configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config
data:
nginx.conf: |
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
|
Ingress Controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| # nginx-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- example.com
secretName: tls-secret
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx-service
port:
number: 80
- path: /api
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: backend-service
port:
number: 8080
|
Persistent Volume for Logs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| # nginx-pv.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nginx-logs-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
hostPath:
path: /var/log/nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nginx-logs-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
|
Complete Kubernetes Deployment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
| # complete-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: nginx-prod
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config
namespace: nginx-prod
data:
default.conf: |
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend-service:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: nginx-prod
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.25-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d
- name: logs
mountPath: /var/log/nginx
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: nginx-config
- name: logs
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nginx-logs-pvc
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
namespace: nginx-prod
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
---
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: nginx-hpa
namespace: nginx-prod
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70
|
Kubernetes Commands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| # Apply configurations
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yaml
kubectl apply -f nginx-configmap.yaml
kubectl apply -f nginx-ingress.yaml
# Check status
kubectl get deployments
kubectl get pods
kubectl get services
kubectl get ingress
# Describe resources
kubectl describe deployment nginx-deployment
kubectl describe pod <pod-name>
kubectl describe service nginx-service
# View logs
kubectl logs <pod-name>
kubectl logs -f <pod-name>
kubectl logs <pod-name> -c nginx
# Execute commands
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- /bin/bash
kubectl exec <pod-name> -- nginx -t
kubectl exec <pod-name> -- nginx -s reload
# Scale deployment
kubectl scale deployment nginx-deployment --replicas=5
# Update deployment
kubectl set image deployment/nginx-deployment nginx=nginx:1.26
# Rollback deployment
kubectl rollout undo deployment/nginx-deployment
kubectl rollout history deployment/nginx-deployment
# Delete resources
kubectl delete -f nginx-deployment.yaml
kubectl delete deployment nginx-deployment
kubectl delete service nginx-service
|
Production-Ready Configuration Examples
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 4096;
use epoll;
multi_accept on;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Logging
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" rt=$request_time';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main buffer=32k flush=5s;
# Performance
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
keepalive_requests 100;
reset_timedout_connection on;
# Buffers
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_header_buffer_size 1k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 8k;
# Timeouts
client_body_timeout 12s;
client_header_timeout 12s;
send_timeout 10s;
# Gzip
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml text/javascript
application/json application/javascript application/xml+rss;
gzip_min_length 256;
# Open file cache
open_file_cache max=10000 inactive=30s;
open_file_cache_valid 60s;
open_file_cache_min_uses 2;
open_file_cache_errors on;
# Security headers
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
# Rate limiting
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=general:10m rate=10r/s;
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
# Hide version
server_tokens off;
# Include virtual hosts
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
|
Secure SSL/TLS Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
# SSL certificates
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/chain.pem;
# SSL configuration
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# DH parameters
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/ssl/dhparam.pem;
# Session cache
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_tickets off;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 valid=300s;
resolver_timeout 5s;
# Security headers
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "strict-origin-when-cross-origin" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';" always;
# Static files
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|eot)$ {
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable";
access_log off;
}
# Main application
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
}
|
Microservices API Gateway
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
| upstream user_service {
least_conn;
server user-service1:8080;
server user-service2:8080;
keepalive 32;
}
upstream order_service {
least_conn;
server order-service1:8080;
server order-service2:8080;
keepalive 32;
}
upstream product_service {
least_conn;
server product-service1:8080;
server product-service2:8080;
keepalive 32;
}
# Rate limiting zones
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=api_limit:10m rate=100r/s;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=strict_limit:10m rate=10r/s;
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name api.example.com;
# SSL configuration
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/api.example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/api.example.com.key;
# Logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/api_access.log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/api_error.log warn;
# CORS headers
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '$http_origin' always;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' 'GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS' always;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' 'Authorization, Content-Type' always;
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000 always;
# Handle preflight
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
return 204;
}
# User service
location /api/users {
limit_req zone=api_limit burst=20 nodelay;
proxy_pass http://user_service;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Timeouts
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
}
# Order service
location /api/orders {
limit_req zone=api_limit burst=20 nodelay;
proxy_pass http://order_service;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# Product service
location /api/products {
limit_req zone=api_limit burst=20 nodelay;
proxy_pass http://product_service;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# Health check
location /health {
access_log off;
return 200 "OK\n";
add_header Content-Type text/plain;
}
}
|
Best Practices Summary
Configuration Management
- Organize configuration files: Use separate files for different contexts
- Use includes: Modularize configuration with
include directives - Comment extensively: Document complex configurations
- Version control: Keep configurations in Git
- Test before deploy: Always run
nginx -t before reload - Backup configurations: Maintain backups of working configurations
- Optimize worker processes: Set to number of CPU cores
- Enable caching: Cache both static and dynamic content appropriately
- Use compression: Enable gzip/brotli for text content
- Configure keepalive: Reduce connection overhead
- Tune buffers: Adjust based on workload characteristics
- Enable sendfile: For efficient static file serving
Security Best Practices
- Keep Nginx updated: Apply security patches promptly
- Use strong SSL/TLS: TLS 1.2/1.3 with modern ciphers
- Implement rate limiting: Protect against abuse
- Hide server information: Disable
server_tokens - Restrict access: Use IP whitelisting and authentication
- Set security headers: Implement all relevant security headers
- Regular audits: Review logs and configurations regularly
Monitoring Best Practices
- Enable comprehensive logging: Log what matters
- Use structured logging: JSON format for aggregation
- Monitor key metrics: Response times, error rates, cache hits
- Set up alerts: Proactive monitoring of critical issues
- Review logs regularly: Identify patterns and issues
- Use monitoring tools: Integrate with Prometheus, Grafana, etc.
References
- Nginx Official Documentation
- Nginx Admin Guide
- Mozilla SSL Configuration Generator
- Nginx Optimization Guide - DigitalOcean
- Nginx Load Balancing Documentation
- Nginx Caching Guide
- Nginx FastCGI Module
- OWASP Nginx Security Headers
- Nginx Performance Tuning
- HTTP/2 Server Push with Nginx
- Nginx Logging Documentation
- Nginx Rewrite Module
- Nginx Stream Module Documentation
- Nginx Best Practices - GitHub
Nginx Community Forum
- Nginx Official Documentation
- Nginx Admin Guide
- Mozilla SSL Configuration Generator
- Nginx Optimization Guide - DigitalOcean
- Nginx Load Balancing Documentation
- Nginx Caching Guide
- Nginx FastCGI Module
- OWASP Nginx Security Headers
- Nginx Performance Tuning
- HTTP/2 Server Push with Nginx