📘 DSML: Machine Learning Workflow & Lifecycle Illustrated
Concise, clear, and validated revision notes on the end-to-end Machine Learning Lifecycle — phases, checklists, pitfalls, and trusted references.
🧭 DSML: Machine Learning Workflow & Lifecycle Illustrated
— Comprehensive Notes: Phases, Jargon, and Best Practices
A structured, novice-friendly guide to understanding the entire Machine Learning Lifecycle — from problem definition to monitoring and governance.
🎯 Overview
The Machine Learning (ML) lifecycle is a structured, iterative process that defines how ML projects move from concept → deployment → continuous improvement.
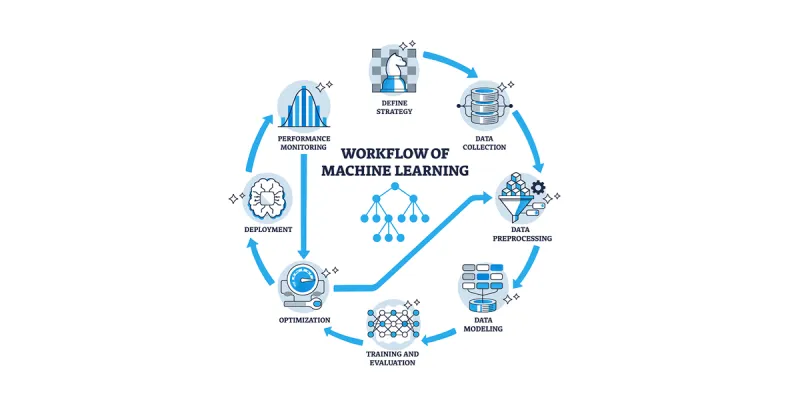
 Machine Learning Lifecycle Illustrated
Machine Learning Lifecycle Illustrated
🧭 Workflow of Machine Learning
A visually guided overview of the Machine Learning Lifecycle, showing each stage in a cyclical, iterative process from strategy to deployment and monitoring.
The ML lifecycle is not linear — it’s a continuous feedback loop where monitoring insights drive retraining and improvement. It ensures reproducibility, reliability, and business value — uniting Data Science, Engineering, and Operations (MLOps).
🧩 Stages in the ML Workflow
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Define Strategy | Establish problem scope, objectives, and metrics. |
| Data Collection | Gather relevant, representative, and reliable data. |
| Data Preprocessing | Clean, transform, and prepare data for modeling. |
| Data Modeling | Select algorithms and structure data relationships. |
| Training & Evaluation | Train models, assess performance using metrics. |
| Optimization | Tune hyperparameters and improve generalization. |
| Deployment | Push trained models into production environments. |
| Performance Monitoring | Continuously track model health and drift. |
- Use MLOps pipelines for automation of retraining and deployment.
- Implement data versioning and experiment tracking for reproducibility.
- Include monitoring tools (EvidentlyAI, WhyLabs, Prometheus) for drift detection.
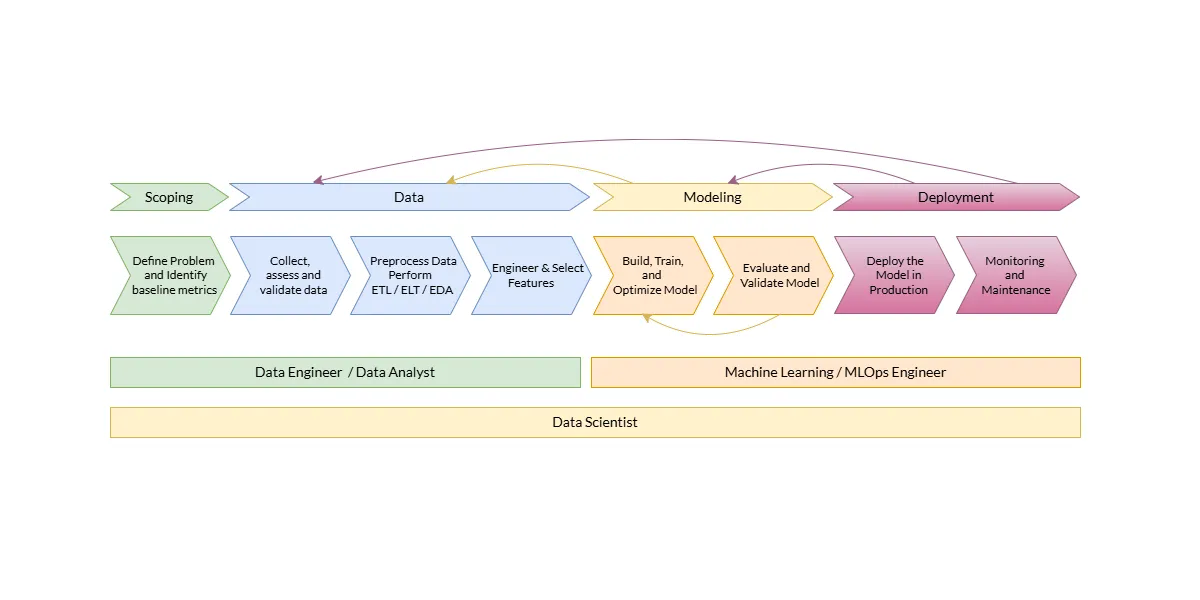
🧩 Canonical Lifecycle Phases
| # | Phase | Objective | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | Problem Definition | Define business problem, goals, and metrics. | Success KPIs, scope, and plan. |
| 2️⃣ | Data Collection & Understanding | Gather, label, and validate datasets. | Data sources, quality report. |
| 3️⃣ | Data Preparation & EDA | Clean, transform, and explore data. | Cleaned data, insights, baselines. |
| 4️⃣ | Feature Engineering & Selection | Create and select meaningful features. | Feature store, importance report. |
| 5️⃣ | Model Development / Experimentation | Build, train, and optimize models. | Model artifacts, logs, metrics. |
| 6️⃣ | Evaluation & Validation | Assess models on performance and fairness. | Validation report, model card. |
| 7️⃣ | Deployment / Productionization | Deploy model into live environment. | APIs, pipelines, documentation. |
| 8️⃣ | Monitoring & Maintenance | Detect drift, retrain, ensure governance. | Monitoring dashboards, alerts. |
🧠 Lifecycle = Iterative Feedback Loop
Each stage informs and improves the next — fostering a continuous learning system.
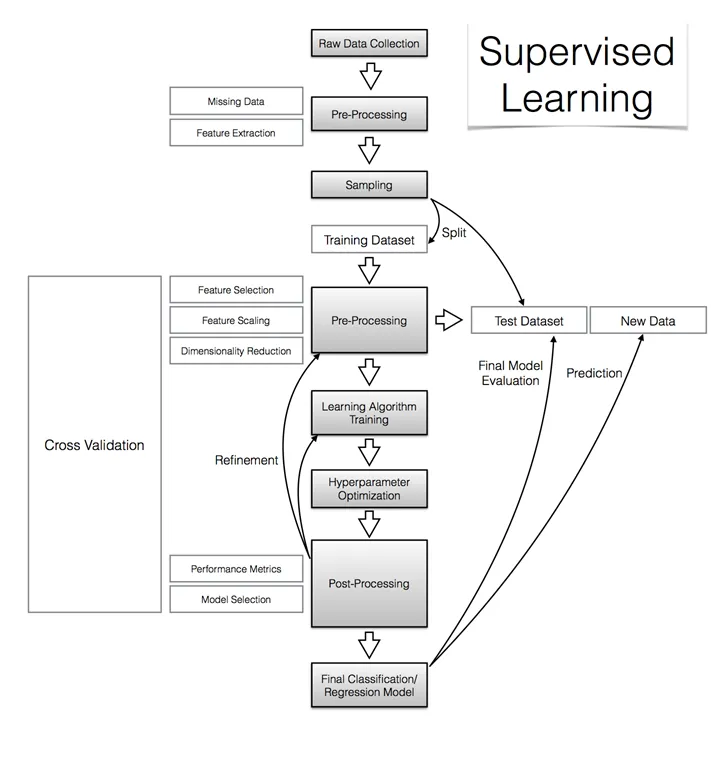 Supervised Learning Steps… Illustrated!
Supervised Learning Steps… Illustrated!
- Courtesy: Sebastian Raschka | Substack
🔤 Jargon Mapping Table
| 💬 Common Jargon / Term | 🎯 Equivalent Lifecycle Phase | 🧩 Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Business Understanding | Problem Definition | Clarifying objectives and success criteria |
| Data Ingestion / ETL | Data Collection & Prep | Importing and transforming data |
| Data Wrangling / Cleaning | Data Preparation | Handling missing values, duplicates |
| Feature Engineering | Feature Stage | Creating model-ready variables |
| Experimentation | Model Development | Training multiple models with tracking |
| Model Selection | Evaluation & Validation | Choosing best model & metrics |
| Serving / Inference | Deployment | Making predictions available |
| Drift Detection | Monitoring | Identifying data/model changes |
| MLOps | Governance & Ops | Managing ML reliably in production |
| Model Registry | Deployment Ops | Versioned model artifact management |
⚙️ Different organizations may use varied terminology — but the underlying workflow remains the same.
🧱 Hierarchical Differentiation Table
| 🔝 Level | 🧩 Sub-Phases | 🎯 Primary Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Design / Strategy | Problem Definition, Goal Alignment | Project charter, success metrics |
| Data Layer | Data Collection, Validation, EDA | Clean dataset, metadata |
| Feature Layer | Feature Engineering, Selection | Feature store, versioned logic |
| Model Layer | Model Training, Experimentation | Model artifacts, experiment logs |
| Evaluation Layer | Validation, Robustness, Fairness | Model card, validation report |
| Production Layer | Deployment, Scaling, CI/CD | APIs, pipelines, registry |
| Operations Layer | Monitoring, Drift, Retraining | Dashboards, alerts, audit logs |
🧩 These hierarchical layers represent increasing maturity and automation.
🧮 Phase-by-Phase Cheat Sheet
1️⃣ Problem Definition
- Align stakeholders and success metrics (business ↔ ML).
- Define hypothesis, constraints, and ethical guidelines.
- 🧾 Deliverables: KPIs, roadmap, data access plan.
2️⃣ Data Collection & Understanding
- Collect, label, and validate datasets.
- Assess data coverage, bias, and quality.
- 🧾 Deliverables: Raw data + quality report.
3️⃣ Data Preparation & EDA
- Handle missing values, outliers, normalization.
- Perform exploratory analysis and visualization.
- 🧾 Deliverables: Clean dataset + EDA summary.
4️⃣ Feature Engineering
- Encode categorical variables.
- Create domain-specific features.
- Apply feature selection techniques.
- 🧾 Deliverables: Feature table, correlation matrix.
5️⃣ Model Development / Training
- Train candidate models.
- Apply hyperparameter tuning and experiment tracking.
- 🧾 Deliverables: Trained model artifacts, logs.
6️⃣ Evaluation & Validation
- Evaluate using metrics (F1, ROC-AUC, RMSE, etc.).
- Conduct error and bias analysis.
- 🧾 Deliverables: Model report, reproducible evaluation.
7️⃣ Deployment / Productionization
- Containerize model (Docker, K8s).
- Automate pipelines (CI/CD).
- 🧾 Deliverables: API endpoint, registry entry.
8️⃣ Monitoring & Governance
- Track drift, latency, fairness, uptime.
- Automate retraining.
- 🧾 Deliverables: Monitoring dashboard, audit trail.
🚀 Typical Tools & Components
| 🧰 Function | ⚙️ Tools / Platforms |
|---|---|
| Data Ingestion | Apache Airflow, Kafka, dbt |
| Feature Store | Feast, Tecton |
| Experiment Tracking | MLflow, Weights & Biases, Comet, Neptune.ai |
| Deployment | Docker, Kubernetes, Vertex AI, Sagemaker, BentoML |
| Monitoring | EvidentlyAI, Prometheus, Grafana, WhyLabs |
| CI/CD | GitHub Actions, Jenkins, ArgoCD, Kubeflow Pipelines |
⚠️ Common Pitfalls & Fixes
| ❌ Pitfall | ✅ Solution |
|---|---|
| Starting without clear metrics | Define measurable success criteria first |
| Data leakage between train/test | Separate sets, temporal split |
| Ignoring model monitoring | Add drift detection, live metrics |
| Untracked experiments | Use MLflow or Comet for traceability |
| Neglecting fairness | Add bias checks & model cards |
🧩 Example (Conceptual)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Define pipeline steps (conceptual)
def ml_pipeline():
data = collect_data()
clean = prepare_data(data)
features = engineer_features(clean)
model = train_model(features)
validate(model)
deploy(model)
monitor(model)
🧠 Every ML pipeline is cyclical: models evolve as data and context change.
📜 Lifecycle in One Line
Plan → Data → Prepare → Feature → Model → Evaluate → Deploy → Monitor → Repeat
🪶 References (Trusted & Validated)
- GeeksforGeeks — Machine Learning Lifecycle
- DataCamp — The Machine Learning Lifecycle Explained
- Deepchecks — Understanding the Machine Learning Life Cycle
- TutorialsPoint — Machine Learning Life Cycle
- Analytics Vidhya — Machine Learning Life Cycle Explained
- Comet ML — ML Lifecycle Platform Guide
- Neptune.ai — The Life Cycle of a Machine Learning Project
🏁 Final Thoughts
🧭 The Machine Learning Lifecycle is the bridge between experimentation and production. It ensures that ML solutions are reliable, explainable, and maintainable — enabling sustainable Data Science success.